P3 Science – Magnets Activity Sheet
You can download this Resource in PDF format to print or keep for future reference. Once you’ve submitted your request, it’ll be delivered straight to your email inbox.
Is your child struggling with understanding magnets in Primary 3 Science?
Magnets may seem simple, but many children find it tricky to remember which materials are magnetic, how magnetic force works, or why magnets behave a certain way.
These revision notes and activity sheets are designed to help your child actively explore magnetic properties through clear explanations and hands-on tasks, just like those they may encounter in school.
In this guide, your child will:
- Learn to identify which materials are magnetic
- Understand the properties and behaviour of magnets
- Observe how magnets can attract without touching
- Recognise real-life uses of magnets in daily life
Why this matters:
Activities like these not only strengthen classroom learning, they also prepare your child for Practical Task Assessments whereby students are expected to observe, predict, record, and explain using scientific thinking.
Let’s explore how magnets work through fun hands-on activities! Use a bar magnet for these investigations.
Activity 1: Magnetic or Non-Magnetic Material?
Instructions: Collect the items listed below. Bring each item close to the magnet.
- Put a tick if the item is attracted to the magnet.
- Put a cross if the item is not attracted.
✏ Add notes (e.g. material)
Item | Magnetic? (✔ / ✘) | Notes (What is it made of?) |
Paper clip | ||
Plastic ruler | ||
Steel spoon | ||
Rubber band | ||
Wooden stick |
Think about it: What do the magnetic items have in common?
- A magnet can be made of magnetic materials such as iron or steel.
- A magnet can attract magnetic materials such as iron and steel.
- Magnets do not attract non-magnetic materials such as aluminium, copper, gold, wood, glass, cloth, rubber and plastics.
Activity 2: Poles of a Magnet – Attract or Repel?
Instructions: Use two bar magnets. Test these combinations:
Combination | Attract / Repel? | Observation Notes |
N – N | ||
S – S | ||
N – S |
How do magnets interact with each other?
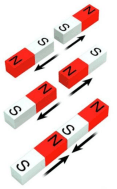
- A magnet has two poles: N-pole and S-pole.
- Magnets can attract or repel each other.
- Unlike poles of magnets (one N-pole and one S-pole) attract each other. • Like poles of magnets (two N-poles or two S-poles) repel each other.
- If a magnet is allowed to turn freely, it will come to rest in the North-South direction.
Activity 3: Magnetic Force at a Distance
Instructions: Place a paperclip on the table. Slowly move the magnet closer to the paperclip without touching it.
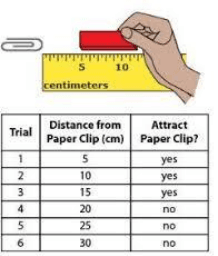
- At what distance did the paperclip start to move?
Magnets can attract certain objects without touching them. This is because magnetic force can act from a distance.
- What does the results of experiment tell you about how magnets work?
The further away the magnet can attract the same magnetic material, the stronger the magnet.
Activity 4: Magnets in Daily Life
Where can magnets be found in objects around us? How are magnets useful?
Magnets are used in a compass to allow us to find directions.
Inside every compass is a tiny, magnetised needle. That means the needle is actually a magnet!
Magnets are used in a compass to allow us to find directions
Inside every compass is a tiny, magnetised needle. That means the needle is actually a magnet!
Here’s how it works:
- The Earth acts like a giant magnet. It has a North Pole and a South Pole.
- The magnet inside the compass is free to spin. One end of the needle is always pulled to point North because of the Earth’s magnetic field.
- Therefore, when you look at a compass, the needle helps you know where North is, and from there, you can find South, East, and West.
Magnets are used in Maglev trains to allow trains to float above the tracks.
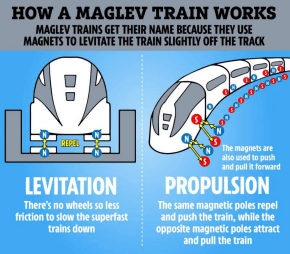
Here’s how it works:
- Floating (Levitation):
- The train and the track both have strong magnets.
- The magnets repel (push away) from each other as their like poles are facing each other. This lifts the train off the track so it floats!
- Moving Forward:
- More magnets are placed along the track. These magnets push the train forward using magnetic force.
- Why is it special?
- The train does not come into contact with the track, so there is no friction between the train and the tracks. Therefore, it can go very fast and very smoothly!
Note: You can download this guide in PDF format to print or keep for future reference. Once you’ve submitted your request, it’ll be delivered straight to your email inbox.